Structural Turbine Design
A structural turbine model in QBlade is defined by a set of ASCII input files that describe the overall dimensions of the turbine and the structural properties of the various turbine components. Structural properties in this sense relates broadly to the mass, inertia, stiffness and damping properties that are required by the structural simulation engine to resolve the structural dynamics. In most cases these structural properties need to be obtained from specialized software, for example software that is build to design a structural blade layout and can generate the cross-sectional mass, stiffness and damping properties that are required to setup a structural model in QBlade. An overview of the how the turbine structure is modeled through the integration of Project-CHRONO in QBlade can be found in the section: Multi Body Beam Formulation.
A structural model may be loaded into a turbine definition by loading the structural model main file through the open file dialog. When a structural model has been assigned to a turbine the structural model files may be examined by clicking View/Edit Struct. The dialog that shows the file contents can also be used to quickly change parameters of the structural model, without the need to modify and save the file outside of QBlade and then importing them again. This edit functionality however doesn’t cause to reload files from the file system, such that changing the string of a blade parameter table doesn’t lead to reloading the newly defined filename. Generally, it is recommended to only use this edit functionality to quickly change a few parameters, but to setup and work with the structural model files outside of QBlade in a text editor.
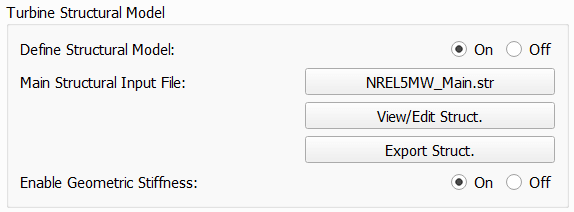
Fig. 72 The structural model dialog.
An overview of the file structure of the structural model definition files is shown in Fig. 73. The main input file needs to be loaded through the dialog. It contains the main turbine parameters and the location of the structural data tables for the definition of the tower and the blades.
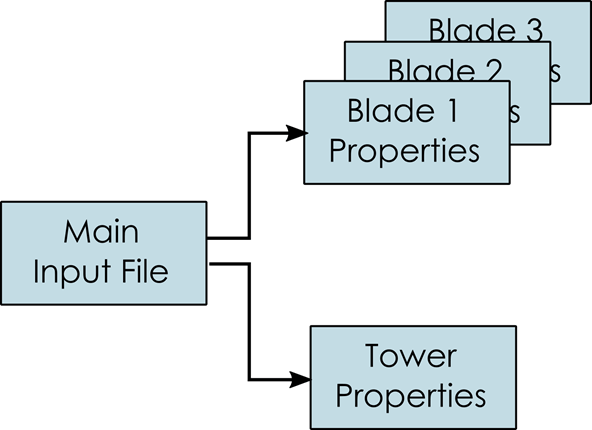
Fig. 73 The file structure of the structural model input files.
Main Definition File
Within the main definition file the overall dimensions of the wind turbine are defined. Furthermore, nacelle mass and inertia and drivetrain properties are defined here. The main input file also contains the file locations of the structural data tables that define the detailed structural properties of the blades, tower and the torquetube (for a VAWT turbine). An overview of important parameters that define the turbine geometry and dimensions is shown in Fig. 74 and Fig. 77.
An exemplary main structural input file for the NREL 5MW HAWT wind turbine is shown below and will be discussed in more detail in the following:
---------------------- QBLADE STRUCTURAL MODEL INPUT FILE -----------------
NREL 5MW Turbine
------------------------------- CHRONO PARAMETERS -------------------------
0.2 GLBGEOEPS - Global geometry epsilon for node placement
------------------------------- HAWT TURBINE CONFIGURATION ----------------
2.5 PRECONE - Rotor PreCone (deg) (HAWT only)
5 SHFTTILT - Turbine Shaft Tilt (deg) (HAWT only)
5.0191 OVERHANG - Rotor Overhang (m) (HAWT only)
1.96256 TWR2SHFT - Tower to Shaft distance (m) (HAWT only)
------------------------------- MASS AND INERTIA --------------------------
0.0 YAWBRMASS - Yaw Bearing Mass (kg) (HAWT only)
240000 NACMASS - Nacelle Mass (kg) (HAWT only)
1.9 NACCMX - Downwind distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CM (m) (HAWT only)
0.0 NACCMY - Lateral distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CM (m) (HAWT only)
1.75 NACCMZ - Vertical distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CM (m) (HAWT only)
2607890 NACYINER - Nacelle Yaw Inertia (kg*m^2) (HAWT only)
56780 HUBMASS - Hub Mass (kg)
115926 HUBINER - Hub Inertia (kg*m^2)
------------------------------- DRIVETRAIN MODEL --------------------------
97 GBRATIO - gearbox ratio (N)
1.0 GBOXEFF - gearbox efficiency (0-1)
1.0 GENEFF - generator efficiency (0-1)
true DRTRDOF - model drivetrain dynamics (true / false)
534.116 GENINER - Generator side (HSS) Inertia (kg*m^2)
867637000 DTTORSPR - Drivetrain torsional stiffness (N*m/rad)
6215000 DTTORDMP - Drivetrain torsional damping (N*m*s/rad)
------------------------------- BRAKE MODEL -------------------------------
0 BRKTORQUE - maximum brake torque
0 BRKDEPLOY - brake deploy time (s) (only used with DTU style controllers)
0 BRKDELAY - brake delay time (s) (only used with DTU style controllers)
------------------------------- SENSOR ERRORS -----------------------------
0 ERRORYAW - yaw error (deg) (HAWT only)
0 ERRORPITCH_1 - pitch error blade1 (deg)
0 ERRORPITCH_2 - pitch error blade2 (deg)
0 ERRORPITCH_3 - pitch error blade3 (deg)
------------------------------- BLADES ------------------------------------
3 NUMBLD - Number of blades
NREL5MW_Blade.str BLDFILE_1 - Name of file containing properties for blade 1
NREL5MW_Blade.str BLDFILE_2 - Name of file containing properties for blade 2
NREL5MW_Blade.str BLDFILE_3 - Name of file containing properties for blade 3
------------------------------- TOWER -------------------------------------
77.6 TWRHEIGHT - Height of the tower (m)
OC3_Sparbuoy_Tower.str TWRFILE - Name of file containing properties for the tower
OC3_Sparbuoy_Sub_LPMD.str SUBFILE - Name of the substructure file
------------------------------- DATA OUTPUT TYPES -------------------------
true FOR_OUT - store (local) forces at all chosen locations
true ROT_OUT - store (local) body rotations at all chosen locations
true MOM_OUT - store (local) moments at all chosen locations
true DEF_OUT - store (local) deflections at all chosen locations
true POS_OUT - store (global) positions at all chosen locations
true VEL_OUT - store (global) velocities at all chosen locations
true ACC_OUT - store (global) accelerations at all chosen locations
true LVE_OUT - store (local) velocities at all chosen locations
true LAC_OUT - store (local) accelerations at all chosen locations
------------------------------- DATA OUTPUT LOCATIONS ---------------------
any number, or zero, user defined positions can be chosen as output locations.
Locations can be assigned at any of the following components: blades, struts, tower
and guy cables. See the following examples for the used nomenclature:
BLD_1_1.0 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 100% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.8 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 80% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.5 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 50% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.4 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 40% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.2 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 20% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.0 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 00% normalized radius
BLD_2_1.0 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 100% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.8 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 80% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.5 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 50% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.4 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 40% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.2 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 20% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.0 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 00% normalized radius
BLD_3_1.0 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 100% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.8 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 80% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.5 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 50% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.4 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 40% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.2 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 20% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.0 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 00% normalized radius
TWR_1.00 - exemplary position, tower at 100% normalized height
TWR_0.90 - exemplary position, tower at 90% normalized height
TWR_0.80 - exemplary position, tower at 80% normalized height
TWR_0.70 - exemplary position, tower at 70% normalized height
TWR_0.60 - exemplary position, tower at 60% normalized height
TWR_0.50 - exemplary position, tower at 50% normalized height
TWR_0.40 - exemplary position, tower at 40% normalized height
TWR_0.30 - exemplary position, tower at 30% normalized height
TWR_0.20 - exemplary position, tower at 20% normalized height
TWR_0.10 - exemplary position, tower at 10% normalized height
TWR_0.00 - exemplary position, tower at 0% normalized height
The different sections of the structural model input file will now be briefly discussed.
HAWT Turbine Configuration
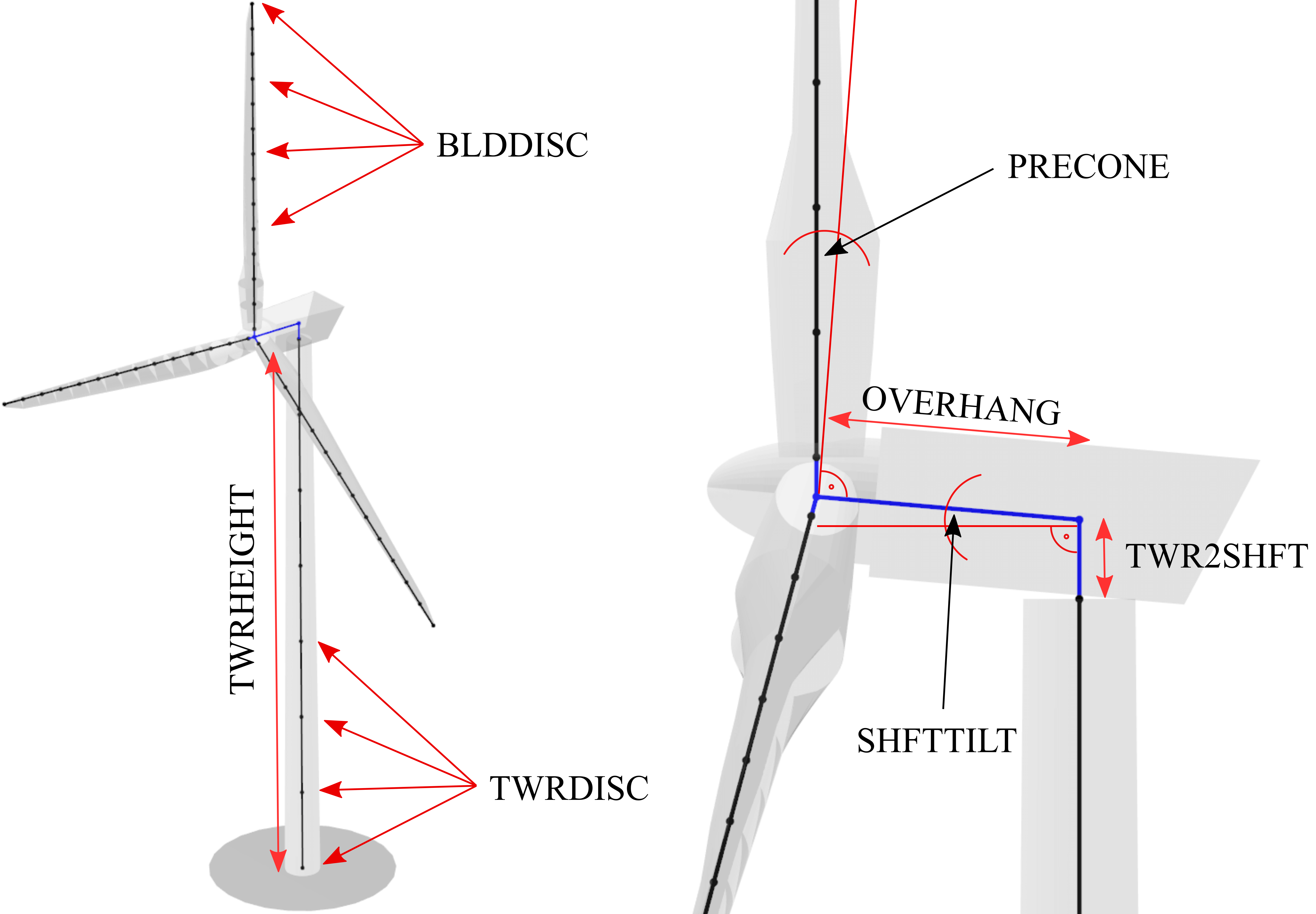
Fig. 74 Overview of geometrical parameters for a HAWT turbine.
------------------------------- HAWT TURBINE CONFIGURATION ----------------
2.5 PRECONE - Rotor PreCone (deg) (HAWT only)
5 SHFTTILT - Turbine Shaft Tilt (deg) (HAWT only)
5.0191 OVERHANG - Rotor Overhang (m) (HAWT only)
1.96256 TWR2SHFT - Tower to Shaft distance (m) (HAWT only)
In this section of the file the main geometrical turbine parameters are defined. These parameters are equivalent to the parameters discussed in Turbine Geometry.
Mass and Inertia Parameters
------------------------------- MASS AND INERTIA --------------------------
0.0 YAWBRMASS - Yaw Bearing Mass (kg) (HAWT only)
240000 NACMASS - Nacelle Mass (kg) (HAWT only)
1.9 NACCMX - Downwind distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CM (m) (HAWT only)
0.0 NACCMY - Lateral distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CM (m) (HAWT only)
1.75 NACCMZ - Vertical distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CM (m) (HAWT only)
2607890 NACYINER - Nacelle Yaw Inertia (kg*m^2) (HAWT only)
56780 HUBMASS - Hub Mass (kg)
115926 HUBINER - Hub Inertia (kg*m^2)
In this section of the input file mass and inertia properties are assigned to the nacelle and the hub. It should be noted here that the parameter HUBINER should only account for the rotational inertia of the hub itself, and not account for the inertia of the rotor blades as this is explicity included through the finite element model.
Nacelle Drag Model
------------------------------- NACELLE DRAG ------------------------------
10.0 NACCAX - Downwind distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CD (m) (HAWT only)
0.0 NACCAY - Lateral distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CD (m) (HAWT only)
1.75 NACCAZ - Vertical distance from the tower-top to the nacelle CD (m) (HAWT only)
15 NACARX - Downwind area of the nacelle (m^2) (HAWT only)
90 NACARY - Lateral area of the nacelle (m^2) (HAWT only)
60 NACARZ - Vertical area of the nacelle (m^2) (HAWT only)
1.2 NACCDX - Downwind drag coefficient of the nacelle (-) (HAWT only)
1.2 NACCDY - Lateral drag coefficient of the nacelle (-) (HAWT only)
1.2 NACCDZ - Vertical drag coefficient of the nacelle (-) (HAWT only)
The nacelle drag model is optional. If no nacelle drag is defined no nacelle drag is applied. The nacelle drag can only be used with HAWT turbine definitions. The model defined a center of drag (NACCA) and three nacelle areas (NACAR) with three nacelle drag coefficients (NACCD). The total acting nacelle drag force in all directions is then summed up and applied at the center of drag (NACCD).
Drivetrain Parameters
------------------------------- DRIVETRAIN MODEL --------------------------
97 GBRATIO - gearbox ratio (N)
1.0 GBOXEFF - gearbox efficiency (0-1)
1.0 GENEFF - generator efficiency (0-1)
true DRTRDOF - model drivetrain dynamics (true / false)
534.116 GENINER - Generator side (HSS) Inertia (kg*m^2)
867637000 DTTORSPR - Drivetrain torsional stiffness (N*m/rad)
6215000 DTTORDMP - Drivetrain torsional damping (N*m*s/rad)
This section of the main input file defined the drive train model. The drive train model in QBlade is a simple 2 mass spring-damper model. An overview is given in Fig. 75. The parameter GBOXEFF define the mechanical losses within the gearbox, GENEFF defined the electrical losses within the generator.
The drivetrain is parameterized by the main shaft torsional stiffness and damping, a high speed side (HSS) generator inertia and the low speed side (LSS) inertia. The LSS inertia (of shaft and Hub combined) should be summed up and assigned to the HUBINER value.
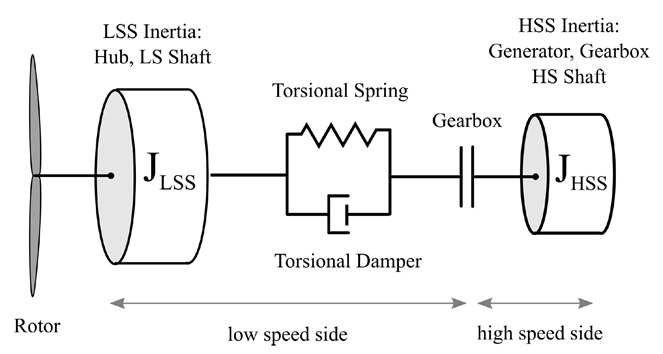
Fig. 75 An overview of the drivetrain model in QBlade.
Brake Model Parameters
------------------------------- BRAKE MODEL -------------------------------
0 BRKTORQUE - maximum brake torque
0 BRKDEPLOY - brake deploy time (s)
0 BRKDELAY - brake delay time (s)
The brake in QBlade is defined as shown above. The brake is parameterized with a delay time, a deploy time and a maximum value for the brake torque. After the brake signal is emitted from the controller, or a brake event, after the delay time (BRKDELAY) has passed the brake is activated and ramped up to the maximum brake torque (BRKTORQUE) during the deploy time (BRKDEPLOY). An overview of this process is shown in Fig. 76.
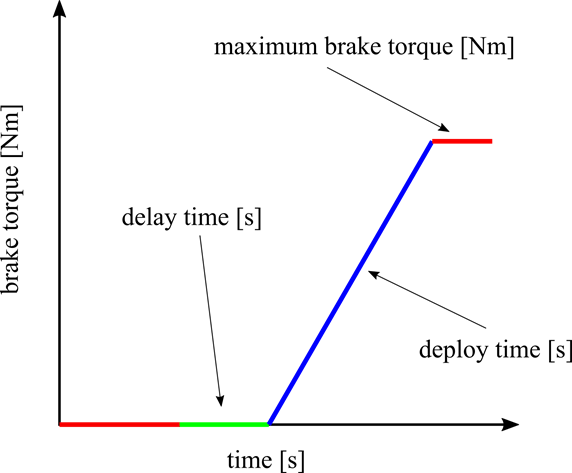
Fig. 76 An overview of the brake model in QBlade.
Modeling Sensor Errors
------------------------------- SENSOR ERRORS -----------------------------
0 ERRORYAW - yaw error (deg) (HAWT only)
0 ERRORPITCH_1 - pitch error blade1 (deg)
0 ERRORPITCH_2 - pitch error blade2 (deg)
0 ERRORPITCH_3 - pitch error blade3 (deg)
Sensor errors are defined for each blade pitch bearing sensor and the yaw bearing sensor. These errors are simply added to the corresponding signals as an offset.
Blade Parameters
------------------------------- BLADES ------------------------------------
3 NUMBLD - Number of blades
NREL5MW_Blade.str BLDFILE_1 - Name of file containing properties for blade 1
NREL5MW_Blade.str BLDFILE_2 - Name of file containing properties for blade 2
NREL5MW_Blade.str BLDFILE_3 - Name of file containing properties for blade 3
The location of the structural data tables for the blades is defined by the keywords shown above. The number of blades is defined by the parameter NUMBLD, this value overrides the number of blades that is defined in the turbine definition dialog. For each blade a keyword BLDFILE_X is searched for where the filename of the blade data table is defined. Different blade data tables can be assigned to each individual blade.
Tower Parameters
------------------------------- TOWER -------------------------------------
77.6 TWRHEIGHT - Height of the tower (m)
OC3_Sparbuoy_Tower.str TWRFILE - Name of file containing properties for the tower
OC3_Sparbuoy_Sub_LPMD.str SUBFILE - Name of the substructure file
The structural tower data table is defined in a similar fashion as for the blades. The keyword TWRHEIGHT defines the absolute height of the tower. The keyword SUBFILE points to a substructure file that can be used to define a more complicated floating or bottom fixed substructure for offshore wind turbines or to model soil dynamics. If the keyword SUBFILE is not defined then the tower will simply be rigidly constrained to the ground. More information on how a substructure file is defined is found in the section: Substructure Design.
VAWT Specific Parameters
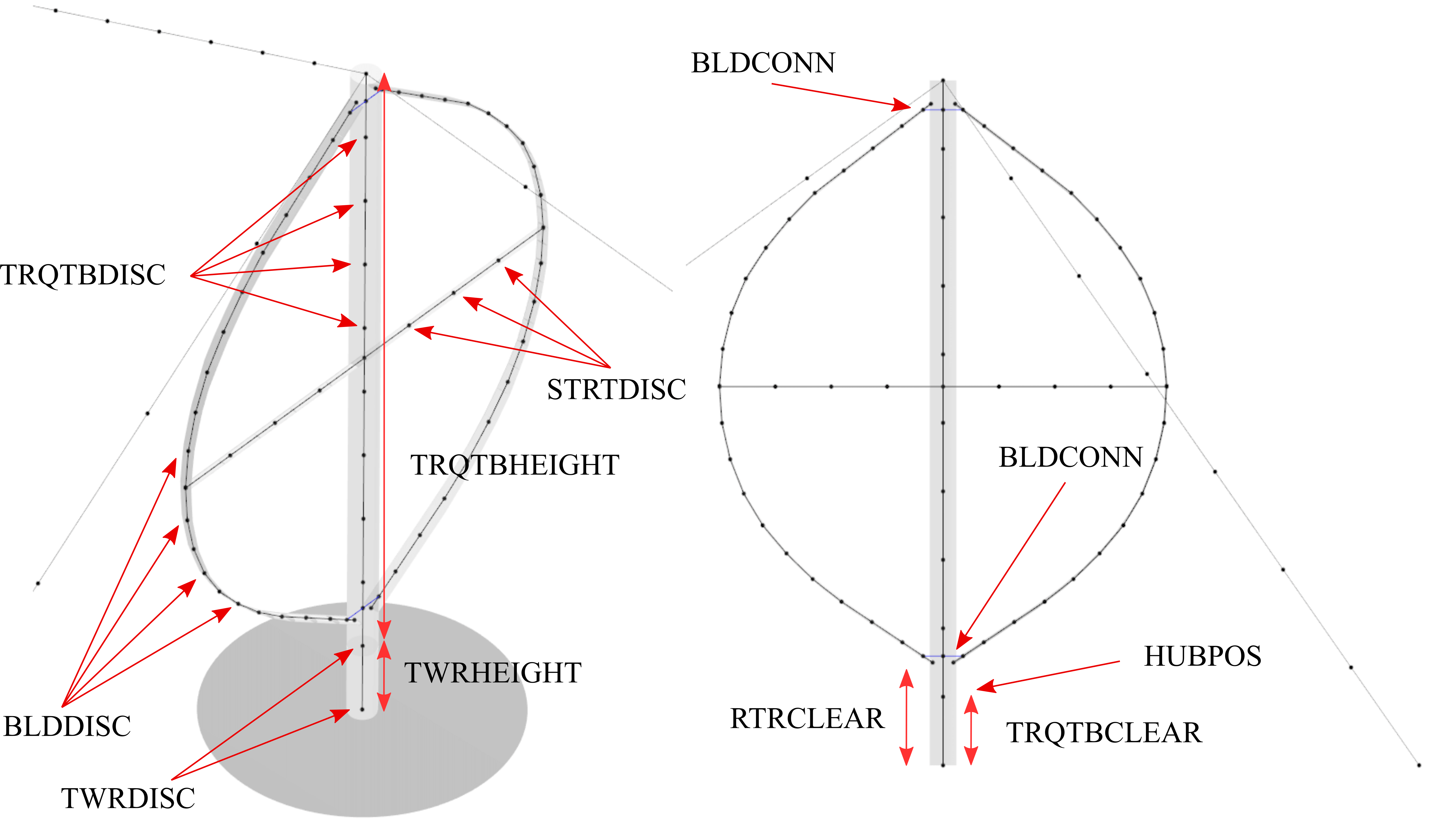
Fig. 77 Overview of geometrical parameters for a VAWT turbine.
Strut Parameters
------------------------------- STRUTS ------------------------------------
strutF100.dat STRTFILE_1 - Name of file containing properties for strut1 (if blade has struts)
strutF100.dat STRTFILE_2 - Name of file containing properties for strut2 (if blade has struts)
Tower and Torquetube Parameters
------------------------------- TOWER AND TORQUE TUBE ---------------------
20.845 TWRHEIGHT - Height of the (fixed - non rotating) tower [m]
tower.dat TWRFILE - Name of file containing properties for the tower
2.4376 TRQTBHEIGHT - Height (or length) of the torque tube (the rotating part of the tower) [m]
torquetube.dat TRQTBFILE - Name of file containing properties for the torque tube
18.427 TRQTBCLEAR - Clearance of the torque tube, must be <= TWRHEIGHT [m]
18.427 HUBPOS - Height of the generator hub that is connecting the torque tube with the fixed tower (VAWT only) [m]
2.4376 TRQTBCONN - Absolute height position, starting after torque tube clearance, of a frictionless bearing that connects the torque tube to the fixed tower [m]
0.5 BLDCONN - Absolute height position, starting after rotor clearance, of blade of the rigid blade torque tube connection 1 in [m] (VAWT only)
40.853 BLDCONN - Absolute height position, starting after rotor clearance, of blade of the rigid blade torque tube connection 2 in [m] (VAWT only)
15.635 RTRCLEAR - Rotor clearance
Cable Parameters
------------------------------- BLDDE CABLES (VAWT only) ------------------
cable.dat CABFILE - file containing the definitions of cables
An exemplary cable definition file is shown here: Cable Definition File.
Loading Data and Sensor Locations
------------------------------- DATA OUTPUT TYPES -------------------------
true FOR_OUT - store (local) forces at all chosen locations
true ROT_OUT - store (local) body rotations at all chosen locations
true MOM_OUT - store (local) moments at all chosen locations
true DEF_OUT - store (local) deflections at all chosen locations
true POS_OUT - store (global) positions at all chosen locations
true VEL_OUT - store (global) velocities at all chosen locations
true ACC_OUT - store (global) accelerations at all chosen locations
true LVE_OUT - store (local) velocities at all chosen locations
true LAC_OUT - store (local) accelerations at all chosen locations
------------------------------- DATA OUTPUT LOCATIONS ---------------------
any number, or zero, user defined positions can be chosen as output locations.
Locations can be assigned at any of the following components: blades, struts, tower
and guy cables. See the following examples for the used nomenclature:
BLD_1_1.0 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 100% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.8 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 80% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.5 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 50% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.4 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 40% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.2 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 20% normalized radius
BLD_1_0.0 - exemplary position, blade 1 at 00% normalized radius
BLD_2_1.0 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 100% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.8 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 80% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.5 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 50% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.4 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 40% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.2 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 20% normalized radius
BLD_2_0.0 - exemplary position, blade 2 at 00% normalized radius
BLD_3_1.0 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 100% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.8 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 80% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.5 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 50% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.4 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 40% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.2 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 20% normalized radius
BLD_3_0.0 - exemplary position, blade 3 at 00% normalized radius
TWR_1.00 - exemplary position, tower at 100% normalized height
TWR_0.90 - exemplary position, tower at 90% normalized height
TWR_0.80 - exemplary position, tower at 80% normalized height
TWR_0.70 - exemplary position, tower at 70% normalized height
TWR_0.60 - exemplary position, tower at 60% normalized height
TWR_0.50 - exemplary position, tower at 50% normalized height
TWR_0.40 - exemplary position, tower at 40% normalized height
TWR_0.30 - exemplary position, tower at 30% normalized height
TWR_0.20 - exemplary position, tower at 20% normalized height
TWR_0.10 - exemplary position, tower at 10% normalized height
TWR_0.00 - exemplary position, tower at 0% normalized height
The last part of the main structural input file deals with the definition of loading data and sensor locations. The locations at which the data will be stored are defined through the following keywords that can be placed anywhere in the structural model main input file:
BLD_X_Y: Stores data for blade X at the normalized curved length position YSTR_X_Y_Z: Stores data for strut Y of blade X at the normalized curved length position ZTWR_X: Stores data for the tower at the normalized curved length position XTRQ_X: Stores data for the torque tube at the normalized curved length position XCAB_X_Y: Stores data for guy cable X at the normalized curved length position Y
Furthermore data is automatically stored at each inter body connection of the model. Each inter body connection is identified by a combination of two body name tags and a z value that gives the height position at which the connection was created during the model definition. In the following two exemplary auto-generated variable names are shown and explained:
- Y l Mom. TRQ - BLD_3 z=29.7m
The moment around the local Y axis at the connection between the torque tube and blade 3, which was defined at a height of 29.7m. This result is given in the local coordinates of the torque tube since the TRQ tag is the first tag in the variable name.
- X l For. STR_2_2 - BLD_2 z=27.5m
This example defines the local reaction force at the connection between the top strut of blade 2 and blade 2, given for the local X axis of the strut.
Nine different data types can be specified to be stored (true) or not (false) at all locations that are specified or automatically generated. These are:
true / false
FOR_OUT: Store the local forces for all locationstrue / false
MOM_OUT: Store the local moments for all locationstrue / false
DEF_OUT: Store the local deflections for all locationstrue / false
ROT_OUT: Store the local accumulated rotations at all chosen locationstrue / false
POS_OUT: Store the global positions for all locationstrue / false
VEL_OUT: Store the global velocities for all locationstrue / false
ACC_OUT: Store the global accelerations for all locationstrue / false
LVE_OUT: Store the local velocities for all locationstrue / false
LAC_OUT: Store the local accelerations for all locations
The forces and moments that obtained from a structural body are the internal shear forces and bending moments. However, the forces and moments given at an inter body connection can be interpreted as the reaction forces and moments acting on the constraint. For an overview of the coordinate systems / conventions in which the simulation results are stored see the section: Coordinate Systems.
Blade, Strut and Tower Structural Data Tables
The cross-sectional beam properties of the blade, tower and strut bodies have to be defined in the form of structural data tables. The definition of the table entries are found in Blade / Strut Structural Data Table Columns and Tower / Torquetube Structural Data Table Columns. An exemplary structural blade data table is shown below:
0.0024 RAYLEIGHDMP
1.00 STIFFTUNER
1.00 MASSTUNER
20 DISC
ADDMASS_0.50 0.00 - add a point mass at relative position 0.50 with 0.00kg mass
LENFRACT_[-] MASSD_[kg/m] EIx_[N.m^2] EIy_[N.m^2] EA_[N] GJ_[N.m^2] GA_[N] STRPIT_[deg] KSX_[-] KSY_[-] RGX_[-] RGY_[-] XCM_[-] YCM_[-] XCE_[-] YCE_[-] XCS_[-] YCS_[-]
0.0000E+00 7.1502E+02 1.8116E+10 1.8116E+10 9.7300E+09 5.5600E+09 6.9500E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 3.2931E-01 3.2936E-01 -4.7995E-05 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00
3.2520E-03 7.1502E+02 1.8116E+10 1.8116E+10 9.7300E+09 5.5600E+09 6.9500E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 3.2931E-01 3.2936E-01 -4.7995E-05 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00
1.9512E-02 8.1446E+02 1.9418E+10 1.9558E+10 1.0790E+10 5.4300E+09 7.7070E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 3.2685E-01 3.2307E-01 7.0102E-03 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00
3.5772E-02 7.7991E+02 1.7458E+10 1.9502E+10 1.0067E+10 4.9900E+09 7.1910E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 3.0601E-01 3.1861E-01 3.8932E-03 0.0000E+00 5.4989E-03 0.0000E+00 5.4989E-03 0.0000E+00
5.2033E-02 7.7937E+02 1.5288E+10 1.9782E+10 9.8672E+09 4.6700E+09 7.0480E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 2.8228E-01 3.1667E-01 5.4728E-03 0.0000E+00 1.5995E-02 0.0000E+00 1.5995E-02 0.0000E+00
6.8293E-02 6.2399E+02 1.0783E+10 1.4854E+10 7.6076E+09 3.4700E+09 5.4340E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 2.6375E-01 3.0599E-01 1.4164E-02 0.0000E+00 2.8457E-02 0.0000E+00 2.8457E-02 0.0000E+00
8.4553E-02 4.7421E+02 7.2296E+09 1.0220E+10 5.4908E+09 2.3200E+09 3.9220E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 2.4658E-01 2.9224E-01 2.5352E-02 0.0000E+00 4.0201E-02 0.0000E+00 4.0201E-02 0.0000E+00
1.0081E-01 4.4659E+02 6.3098E+09 9.1448E+09 4.9714E+09 1.9100E+09 3.5510E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 2.3129E-01 2.8160E-01 3.5071E-02 0.0000E+00 5.1288E-02 0.0000E+00 5.1288E-02 0.0000E+00
1.1707E-01 4.2193E+02 5.5286E+09 8.0626E+09 4.4940E+09 1.5700E+09 3.2100E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 2.1690E-01 2.7057E-01 4.6278E-02 0.0000E+00 6.4150E-02 0.0000E+00 6.4150E-02 0.0000E+00
1.3333E-01 4.0237E+02 4.9798E+09 6.8838E+09 4.0348E+09 1.1600E+09 2.8820E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 2.0504E-01 2.5549E-01 5.5352E-02 0.0000E+00 7.6335E-02 0.0000E+00 7.6335E-02 0.0000E+00
1.4959E-01 4.2090E+02 4.9364E+09 7.0098E+09 4.0376E+09 1.0000E+09 2.8840E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.9141E-01 2.4658E-01 6.7216E-02 0.0000E+00 8.7894E-02 0.0000E+00 8.7894E-02 0.0000E+00
1.6585E-01 4.4898E+02 4.6914E+09 7.1680E+09 4.1692E+09 8.5600E+08 2.9780E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.7635E-01 2.4202E-01 6.8242E-02 0.0000E+00 1.0107E-01 0.0000E+00 1.0107E-01 0.0000E+00
1.8211E-01 4.3897E+02 3.9494E+09 7.2716E+09 4.0824E+09 6.7200E+08 2.9160E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.6368E-01 2.4883E-01 6.6958E-02 0.0000E+00 1.1356E-01 0.0000E+00 1.1356E-01 0.0000E+00
1.9837E-01 4.2777E+02 3.3866E+09 7.0812E+09 4.0866E+09 5.4700E+08 2.9190E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.5436E-01 2.5762E-01 5.8711E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2168E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2168E-01 0.0000E+00
2.1463E-01 4.0169E+02 2.9344E+09 6.2440E+09 3.6680E+09 4.4900E+08 2.6200E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.4756E-01 2.5220E-01 5.9779E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2323E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2323E-01 0.0000E+00
2.3089E-01 3.7157E+02 2.5690E+09 5.0484E+09 3.1472E+09 3.3600E+08 2.2480E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.4153E-01 2.4160E-01 6.8041E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2262E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2262E-01 0.0000E+00
2.4715E-01 3.6805E+02 2.3884E+09 4.9490E+09 3.0114E+09 3.1100E+08 2.1510E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.3776E-01 2.4075E-01 6.9442E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2360E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2360E-01 0.0000E+00
2.6341E-01 3.6496E+02 2.2722E+09 4.8076E+09 2.8826E+09 2.9200E+08 2.0590E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.3583E-01 2.3952E-01 7.0957E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2269E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2269E-01 0.0000E+00
2.9593E-01 3.5737E+02 2.0496E+09 4.5010E+09 2.6138E+09 2.6100E+08 1.8670E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.3211E-01 2.3616E-01 7.3227E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2305E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2305E-01 0.0000E+00
3.2846E-01 3.4754E+02 1.8284E+09 4.2434E+09 2.3576E+09 2.2900E+08 1.6840E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.2843E-01 2.3363E-01 7.8424E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2360E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2360E-01 0.0000E+00
3.6098E-01 3.3910E+02 1.5890E+09 3.9956E+09 2.1462E+09 2.0100E+08 1.5330E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.2363E-01 2.3296E-01 7.8316E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2421E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2421E-01 0.0000E+00
3.9350E-01 3.3050E+02 1.3619E+09 3.7506E+09 1.9446E+09 1.7400E+08 1.3890E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.1868E-01 2.3275E-01 7.8557E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2284E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2284E-01 0.0000E+00
4.2602E-01 3.1040E+02 1.1024E+09 3.4468E+09 1.6324E+09 1.4400E+08 1.1660E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.1139E-01 2.2858E-01 8.7855E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2396E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2396E-01 0.0000E+00
4.5854E-01 3.0238E+02 8.7584E+08 3.1388E+09 1.4322E+09 1.2000E+08 1.0230E+08 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 1.0343E-01 2.2650E-01 8.5572E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2279E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2279E-01 0.0000E+00
4.9106E-01 2.7734E+02 6.8124E+08 2.7342E+09 1.1687E+09 8.1200E+07 8.3480E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 9.6993E-02 2.2246E-01 8.9951E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2425E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2425E-01 0.0000E+00
5.2358E-01 2.6666E+02 5.3466E+08 2.5550E+09 1.0475E+09 6.9100E+07 7.4820E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 9.0303E-02 2.2464E-01 8.8604E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2292E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2292E-01 0.0000E+00
5.5610E-01 2.5451E+02 4.0894E+08 2.3338E+09 9.2302E+08 5.7500E+07 6.5930E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 8.3338E-02 2.2561E-01 8.5360E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2426E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2426E-01 0.0000E+00
5.8862E-01 2.3236E+02 3.1458E+08 1.8284E+09 7.6076E+08 4.5900E+07 5.4340E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 7.9830E-02 2.2268E-01 8.4224E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2569E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2569E-01 0.0000E+00
6.2114E-01 2.1094E+02 2.3870E+08 1.5848E+09 6.4806E+08 3.6000E+07 4.6290E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 7.6068E-02 2.2493E-01 7.9155E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2420E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2420E-01 0.0000E+00
6.5366E-01 1.8894E+02 1.7584E+08 1.3234E+09 5.3970E+08 2.7400E+07 3.8550E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 7.2179E-02 2.2638E-01 7.0245E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2575E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2575E-01 0.0000E+00
6.8618E-01 1.7387E+02 1.2601E+08 1.1837E+09 5.3116E+08 2.0900E+07 3.7940E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6939E-02 2.4642E-01 4.3584E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2414E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2414E-01 0.0000E+00
7.1870E-01 1.6262E+02 1.0725E+08 1.0202E+09 4.6004E+08 1.8500E+07 3.2860E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6508E-02 2.4696E-01 3.6522E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2581E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2581E-01 0.0000E+00
7.5122E-01 1.4632E+02 9.0874E+07 7.9786E+08 3.7576E+08 1.6300E+07 2.6840E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6749E-02 2.4513E-01 4.5051E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2407E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2407E-01 0.0000E+00
7.8374E-01 1.3644E+02 7.6314E+07 7.0966E+08 3.2886E+08 1.4500E+07 2.3490E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6198E-02 2.4839E-01 4.0603E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2588E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2588E-01 0.0000E+00
8.1626E-01 1.1296E+02 6.1054E+07 5.1814E+08 2.4402E+08 9.0700E+06 1.7430E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6835E-02 2.4572E-01 4.5184E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2398E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2398E-01 0.0000E+00
8.4878E-01 1.0403E+02 4.9476E+07 4.5486E+08 2.1154E+08 8.0600E+06 1.5110E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6071E-02 2.5059E-01 3.7078E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2596E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2596E-01 0.0000E+00
8.8130E-01 9.5044E+01 3.9354E+07 3.9508E+08 1.8158E+08 7.0800E+06 1.2970E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.5143E-02 2.5583E-01 2.7860E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2388E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2388E-01 0.0000E+00
8.9756E-01 8.7412E+01 3.4664E+07 3.5378E+08 1.6030E+08 6.0900E+06 1.1450E+07 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.5499E-02 2.5874E-01 2.3511E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2342E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2342E-01 0.0000E+00
9.1382E-01 7.6781E+01 3.0408E+07 3.0478E+08 1.0923E+08 5.7500E+06 7.8020E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.7897E-02 2.3439E-01 5.8270E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2811E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2811E-01 0.0000E+00
9.3008E-01 7.2427E+01 2.6516E+07 2.8140E+08 1.0009E+08 5.3300E+06 7.1490E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.8201E-02 2.4056E-01 5.2444E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2366E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2366E-01 0.0000E+00
9.3821E-01 6.9786E+01 2.3842E+07 2.6166E+08 9.2246E+07 4.9400E+06 6.5890E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.8860E-02 2.4603E-01 5.0497E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2917E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2917E-01 0.0000E+00
9.4634E-01 6.2494E+01 1.9628E+07 1.5876E+08 6.3224E+07 4.2400E+06 4.5160E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 7.0184E-02 2.2737E-01 7.8974E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2693E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2693E-01 0.0000E+00
9.5447E-01 5.8886E+01 1.6002E+07 1.3789E+08 5.3326E+07 3.6600E+06 3.8090E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.9485E-02 2.3028E-01 7.8893E-02 0.0000E+00 1.3004E-01 0.0000E+00 1.3004E-01 0.0000E+00
9.6260E-01 5.5273E+01 1.2830E+07 1.1879E+08 4.4534E+07 3.1300E+06 3.1810E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.8804E-02 2.3374E-01 7.7403E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2753E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2753E-01 0.0000E+00
9.7073E-01 5.1724E+01 1.0080E+07 1.0163E+08 3.6904E+07 2.6400E+06 2.6360E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.8277E-02 2.3815E-01 7.4901E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2462E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2462E-01 0.0000E+00
9.7886E-01 4.8253E+01 7.5502E+06 8.5064E+07 2.9918E+07 2.1700E+06 2.1370E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.6807E-02 2.4331E-01 7.4254E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2173E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2173E-01 0.0000E+00
9.8699E-01 4.3884E+01 4.6004E+06 6.4260E+07 2.1308E+07 1.5800E+06 1.5220E+06 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 6.1430E-02 2.4597E-01 8.1096E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2205E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2205E-01 0.0000E+00
9.9512E-01 1.2062E+01 2.5004E+05 6.6094E+06 4.8496E+06 2.5000E+05 3.4640E+05 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 5.4262E-02 2.6302E-01 7.4337E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2247E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2247E-01 0.0000E+00
1.0000E+00 1.0867E+01 1.6996E+05 5.0106E+06 3.5294E+06 1.9000E+05 2.5210E+05 0.0000E+00 5.0000E-01 5.0000E-01 4.4641E-02 2.6025E-01 7.1103E-02 0.0000E+00 1.2487E-01 0.0000E+00 1.2487E-01 0.0000E+00
RGBCOLOR
R G B
220 220 220
The keyword RAYLEIGHDMP: defines a stiffness proportional Rayleigh damping coefficient (see Structural (Rayleigh) Damping). The parameters STIFFTUNER and MASSTUNER can be used to tune the global stiffness or mass properties of the data table through a multiplication by this factor. The keyword RGBCOLOR defines the rgb values that are used to color the structural body during the 3D visualization.
The keyword DISC controls the discretization of the body into structural nodes. The following options are available:
<num> DISC: Discretization into <num> equally spaced (along the curved length) structural nodes.struct DISC: The discretization is carried out after the discretization in the structural data table.aero DISC: The discretization is carried out after the discretization in the aerodynamic blade data table (only for blade bodies).
The keyword ADDMASS_<pos> can be used to add a mass at the normalized position <pos>. ADDMASS_<pos> can be followed by up to 7 numeric values (at least one) to assign mass and rotational inertia properties. For example: ADDMASS_0.2 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 adds a mass of 10kg at the normalized position of 0.2. The following numbers assign the rotational inertia in local body coordinates: Ixx = 1, Iyy = 2, Izz = 3, Ixy = 4, Ixz = 5, Iyz = 6.
Structural (Rayleigh) Damping
A Rayleigh damping coefficient can be set for each structural data table by using the keyword RAYLEIGHDMP. This keyword defined the stiffness proportional Rayleigh damping coefficient \(\beta\):
\(C=beta*K\),
where \(C\) the stiffness matrix. The Rayleigh damping \(beta\) coefficient is related to the fraction of critical damping \(Xi\) as:
\(\zeta = \beta * \pi * f\), or
\(\beta = \frac{\zeta}{\Pi * f}\).
Rayleigh damping is not constant, but varies with frequency. Typically, Rayleigh damping is set for the first natural frequency of a component. Optionally, it is also possible to assign a nonuniformly distributed \(\beta\) coefficient via the structural datatables (see Blade / Strut Structural Data Table Columns).
Blade / Strut Structural Data Table Columns
The following table gives an overview of the entries of the structural data table for blades and struts:
Col. Nr. |
Name |
Explanation |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Length |
Curved length distance from the first body node normalized by the body length |
|
2 |
Mass density |
Mass per unit length |
kg/m |
3 |
Bend. stiff. X |
Bending Stiffness around \(X_{ce}\) (\(EI_{xx}\)) |
Nm^2 |
4 |
Bend. stiff. Y |
Bending Stiffness around \(Y_{ce}\) (\(EI_{yy}\)) |
Nm^2 |
5 |
Axial stiff. |
Longitudinal Stiffness (\(EA\)) |
N |
6 |
Tors. stiff. |
Torsional Stiffness (\(GJ\)) |
Nm^2 |
7 |
Shear stiff. |
Shear Stiffness (\(GA\)) (not used with Euler beams) |
N |
8 |
Str. pitch |
Structural pitch angle between reference \(X\) and \(X_{ce}\) axis |
deg |
9 |
Shear factor X |
Shear factor for force in principal bending axis \(X_{ce}\) |
|
10 |
Shear factor Y |
Shear factor for force in principal bending axis \(Y_{ce}\) |
|
11 |
Radius of gyration X |
Norm. radius of inertia corresponding to a rotation around \(X_{ce}\) |
%chord |
12 |
Radius of gyration Y |
Norm. radius of inertia corresponding to a rotation around \(Y_{ce}\) |
%chord |
13 |
Center of mass X |
Norm. center of mass position \(X\) |
%chord |
14 |
Center of mass Y |
Norm. center of mass position \(Y\) |
%chord |
15 |
Center of elast. X |
Norm. center of elasticity position \(X\) |
%chord |
16 |
Center of elast. Y |
Norm. center of elasticity position \(Y\) |
%chord |
17 |
Center of shear X |
Norm. center of shear position \(X\) |
%chord |
18 |
Center of shear Y |
Norm. center of shear position \(Y\) |
%chord |
19 |
Damping Coefficient |
(optional) This column allows to assign distributed Rayleigh beta coeff. |
Tower / Torquetube Structural Data Table Columns
The following table gives an overview of the entries of the structural data table:
Col. Nr. |
Name |
Explanation |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Length |
Curved length distance from the first body node normalized by the body length |
|
2 |
Mass density |
Mass per unit length |
kg/m |
3 |
Bend. stiff. X |
Bending Stiffness around \(X_{ce}\) (\(EI_{xx}\)) |
Nm^2 |
4 |
Bend. stiff. Y |
Bending Stiffness around \(Y_{ce}\) (\(EI_{yy}\)) |
Nm^2 |
5 |
Axial stiff. |
Longitudinal Stiffness (\(EA\)) |
N |
6 |
Tors. stiff. |
Torsional Stiffness (\(GJ\)) |
Nm^2 |
7 |
Shear stiff. |
Shear Stiffness (\(GA\)) (not used with Euler beams) |
N |
8 |
Str. pitch |
Structural pitch angle between reference \(X\) and \(X_{ce}\) axis |
deg |
9 |
Shear factor X |
Shear factor for force in principal bending axis \(X_{ce}\) |
|
10 |
Shear factor Y |
Shear factor for force in principal bending axis \(Y_{ce}\) |
|
11 |
Radius of gyration X |
Norm. radius of inertia corresponding to a rotation around \(X_{ce}\) |
%chord |
12 |
Radius of gyration Y |
Norm. radius of inertia corresponding to a rotation around \(Y_{ce}\) |
%chord |
13 |
Center of mass X |
Norm. center of mass position \(X\) |
%chord |
14 |
Center of mass Y |
Norm. center of mass position \(Y\) |
%chord |
15 |
Center of elast. X |
Norm. center of elasticity position \(X\) |
%chord |
16 |
Center of elast. Y |
Norm. center of elasticity position \(Y\) |
%chord |
17 |
Center of shear X |
Norm. center of shear position \(X\) |
%chord |
18 |
Center of shear Y |
Norm. center of shear position \(Y\) |
%chord |
19 |
Diameter |
Cross section diameter |
m |
20 |
Drag |
(optional) Drag coefficient for aerodynamic drag |
|
21 |
Damping Coefficient |
(optional) This column allows to assign distributed Rayleigh beta coeff. |
Cable Definition File
------------------------------CABLE DATA--------------------------------
CABELEMENTS
CabID MASS_[kg/m] EIy_[N.m^2] EA_[N] DAMP_[-] DIA_[m]
1 1.574300E+00 6.755490E+02 4.222260E+07 0.002 0.016
2 9.048000E-01 1.964547E+02 2.182830E+07 0.002 0.012
CABMEMBERS
ID CONN_1 CONN_2 Tension[N] CabID Drag ElmDsc Name
1 STR_1_1_0.0 STR_1_1_1.0 70000 1 0 2 B1StrutBot
2 STR_2_1_0.0 STR_2_1_1.0 70000 1 0 2 B1StrutTop
3 STR_1_1_1.0 TRQ_0.9631 15000 2 0.99 2 B1TieRod3
4 STR_2_1_1.0 TRQ_0.2839 15000 2 0.99 2 B1TieRod1
5 STR_1_2_0.0 STR_1_2_1.0 70000 1 0 2 B2StrutBot
6 STR_2_2_0.0 STR_2_2_1.0 70000 1 0 2 B2StrutTop
7 STR_1_2_1.0 TRQ_0.9631 15000 2 0.99 2 B2TieRod3
8 STR_2_2_1.0 TRQ_0.2839 15000 2 0.99 2 B2TieRod1
9 STR_1_3_0.0 STR_1_3_1.0 70000 1 0 2 B2StrutBot
10 STR_2_3_0.0 STR_2_3_1.0 70000 1 0 2 B2StrutTop
11 STR_1_3_1.0 TRQ_0.9631 15000 2 0.99 2 B2TieRod3
12 STR_2_3_1.0 TRQ_0.2839 15000 2 0.99 2 B2TieRod1
Cables can be defined between blades (BLD), struts (STR), the tower (TWR), torquetube (TRQ) or the ground (GRD).
Cross Sectional Blade Coordinate System
The local cross-sectional coordinate system for the definition of the blade and strut structural data table is shown in Fig. 78.
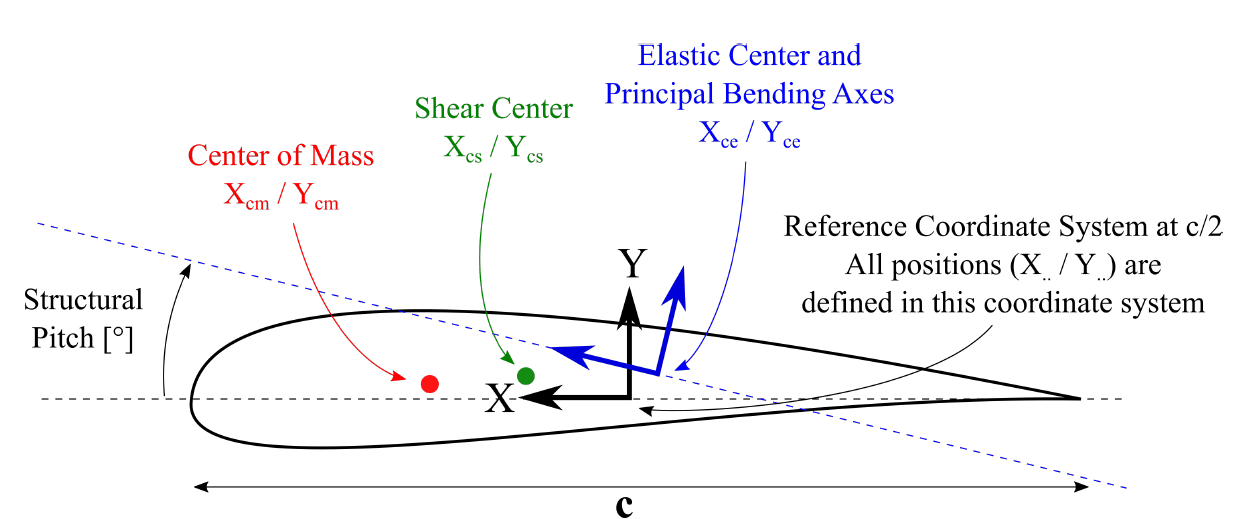
Fig. 78 Visualization of the local coordinate system that is used to define the cross sectional beam properties of blades and struts.
This cross sectional coordinate system in ONLY used for the definition of the blade and strut sectional structural properties! This cross sectional blade or strut coordinate system does NOT coincide with the local blade coordinate system (see Local Blade Coordinate System). The local blade (and strut) coordinate system follows the DNVGL definition 1. The sectional coordinate system shown in Fig. 78 differs from the local body coordinate system (Fig. 79) in the following way:
the local blade X-axis points in the direction of the cross sectional Y-axis.
the local blade Y-Axis points in the direction opposite the cross sectional X-axis.
the local blade Z-Axis points along the blade principal axis towards the blade tip.
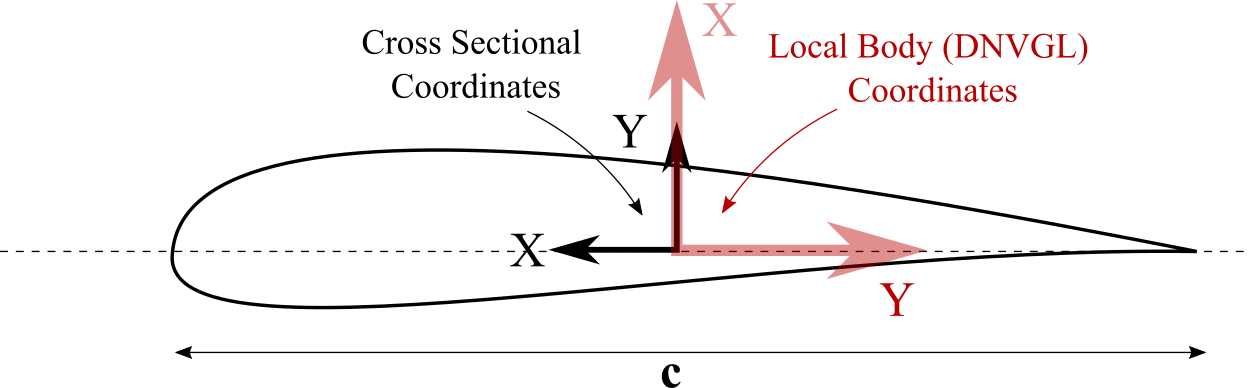
Fig. 79 Difference between the local body coordinate system (DNVGL) and the cross sectional properties coordinate system.
For all other structural bodies (tower, torquetube, substructure) the coordinate system in which the cross sectional structural properties are defined coincides with the local body coordinate system (see Local Blade Coordinate System).
- 1
DNVGL. Guideline for the Certification of Wind Turbines. 2010.