Aerodynamic Turbine Design
This section covers all options that are related to the aerodynamic modelling of a turbine design. Covering wake models, dynamic stall models, geometry parameters and blade discretization.
Turbine Geometry
If no structural model is defined for this turbine object the turbine geometry is defined here. If a structural model is defined the geometry is defined within the structural model files.
Rotor Overhang: Sets the rotor overhang of the turbine object (see Fig. 69)
Tower Height: Definition of the tower height.
Tower Top/Bottom Radius: Defined the tower top and bottom radius. A linear interpolation is applied for all tower stations in between.
Rotor Shaft Tilt Angle: Sets the rotor shaft tilt angle (see Fig. 69).
Rotor Cone Angle: Sets the rotor cone angle (see Fig. 69).
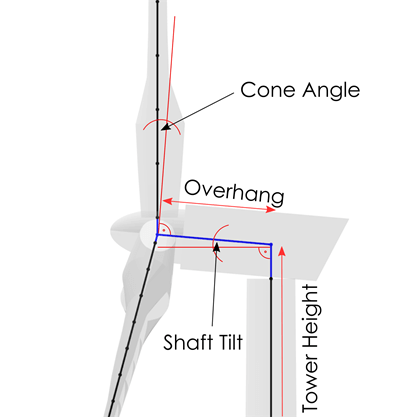
Fig. 69 Definition of turbine geometry parameters.
Aerodynamic Discretization
Blade Panels: Here the user can specifiy the number of blade panels and the type of spacing. A Linear spacing distribues the panels evenly over the blade length. A Cosine spacing results in a finer discretization near the blade ends (root and tip) and a slighly coarser discretization near the blade center. The option Table uses the aerodynamic blade definition table as a temnplate for the aerodynamic discretization, thus the user can use this option for a fully customized blade discretization.
Aerodynamic Models
Dynamic Stall: The user can activate the use of a dynamic stall model. The options are: Off: No dynamic stall model is used. OYE: The OYE dynamic stall model is used, see OYE Model. ATEF: The ATEFlap unsteady aerodynamics model is used, see ATEFlap Model.
2 Point L/D Eval: This actives the two point lift and drag evaluation model, proposed by Li et al.1. The advantage of this two point evaluation is that lift and drag predictions for dihedral or conned wind turbine rotor are improved and the airfoil pitch rate is explicitly being taken into account by evaluating the angle of attack at the three-quarter chord point and then applying the aerodynamic coefficients at the quarter-chord point.
Himmelskamp Effect: The correction for the Himmelskamp effect can be activated here, see Himmelskamp Effect.
Tower Shadow: The Tower Shadow Effect can be avtivated, see Tower Influence.
Tower Drag Coeff.: Sets the drag coefficient that is used to model the Tower Shadow Effect.
Wake Type
Here the user can choose between the Free Vortex Wake or the Unsteady BEM aerodynamic model. The Unsteady BEM model can only be used with HAWT turbine definitions.
Unsteady BEM
The Blade Element Momentum Method in QBlade is the default modeling option for HAWT (Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines). It has a large computational efficiency and good accuracy in most cases. The Unsteady BEM cannot be used to model VAWT (Vertical Axis Wind Turbines). To model a VAWT the Free Vortex Wake method must be used.
Unsteady BEM Options
Azimuthal Polar Grid Discretization: The polar grid is discretized into the chosen number of azimuthal sections. A value of 1 is equal to the BEM without a polar grid.
Include Tip Loss: This activates the classical BEM tip loss correction to account for a finite number of blades, see Glauert2.
Convergence Acceleration Time: The time lag constants in the unsteady BEM implementation are increased by a factor of 20 during the time span entered by the user. This enables a much faster convergence of the unsteady BEM towards a steady operational point.
The theory of the unsteady polar BEM is briefly described in Polar Grid.
Free Vortex Wake
The Lifting Line Free Vortex Wake method in QBlade yields an improved accuracy over the Unsteady BEM method, especially for unsteady operating conditions, such as changing inflow speed or direction or floating wind turbines, that are subjected to wave forces. This increased fidelity however comes at an increased computational cost. Furthermore, the number of settings that are required to setup this method is significantly larger than the BEM settings. All LLFVW modeling options are detailed in the following.
Wake Modelling
Wake Integration Type: This sets the velocity integration method for the wake nodes during the free wake convection step. EF: A simple 1st Order Euler Forward integration. PC: A 2nd Order Predictor Corrector integration method. PC2B: A second Order Predictor Corrector Backwards integration scheme.
Wake Rollup: This actives or deactivates the wake self-induction.
Include Trailing/Shed Vortices: This sets if trailing (streamwise) or shed (spanwise) vortices are generated at the blades trailing edge during every timepstep.
Wake Convection: The user can choose here which free-stream velocity contributes to the total convection velocitzy of the wake nodes. BL: The convection velocity is the mean boundary layer velocity (as a function of height). HH: The convection velocity is the constant hub-height velocity. LOC: The convection velocity is evaluated locally at each wake node position.
Wake Relaxation Factor: This factor can be used to relax the wake by blending out the starting vortex. The factor controls how long the wake is allowed to be after a given number of rotor revolutions or timesteps (depending on the Count Wake Length In setting). Such as a value of 0.5 allows for a wake length of 5 revolutions after the rotor has undergone 10 revolutions. A factor of 1 deactivaes the blending.
First Wake Row Length Factor: This factor can be used to assign a shortened length to the newly created wake elements at the trailing edge so that the newly created shed vorticity is in closer proximity to the blade. A factor of 1 deactivates the shortening.
Max Num. Elements / Norm. Distance: These two values are used to cut-off the wake after a fixed numbner of vortex elements has been created (Max. Num. Wake Elements) or after a vortex element has reached a distance (normalized by rotor diameter) from the hub that is larger than Norm. Distance.
Wake Reduction Factor: This factor filters out wake elements that have a circulation smaller than the maximum circulation in the wake multiplied by this factor. In most cases this effectively removes shed vorticity that does not significantly affect the wake induction (see Fig. 70).
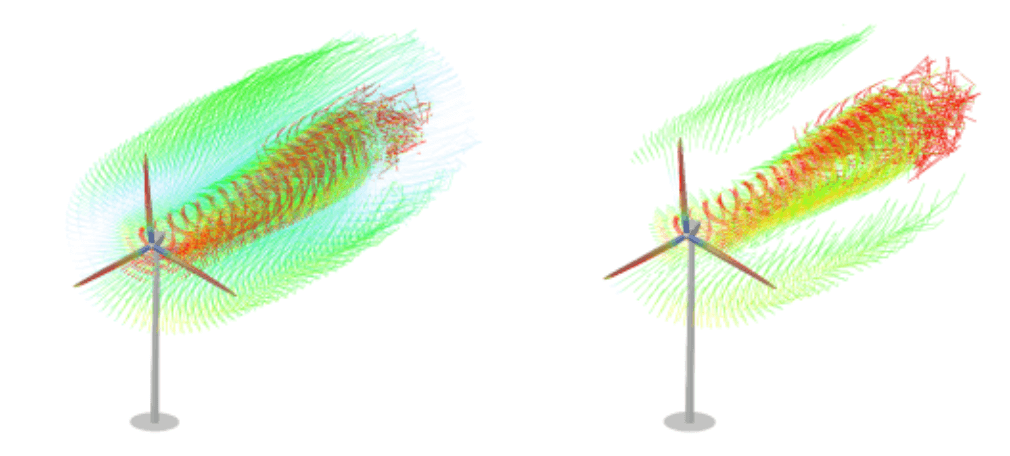
Fig. 70 Visualization of the wake reduction approach.
Count Wake Length In: This setting controls how the age of a vortex element is counted. Either as a number of rotor revolutions, or as a number of timesteps that have passed since the elemnt was created.
Particle Conversion after [Revolutions/Timesteps]: (Only QBlade-EE) This setting controls when a vortex filament is converted into a vortex particle. If the vortex elemnt has reached an age (in timesteps or revolutions) equal to this value it is converted into a particle.
Wake Zones N/1/2/3 in [Revolutions/Timesteps]: This setting controls the length of the different wake zones. The length is either counted in rotor revolutions or in timesteps, depending on the setting (Count Wake Length In). Each wake zone has a successively coarser discretization (depending on the Wake Zones Factor settings) to reduce the total number of free wake elements and thereby to speed up the simulation.
Wake Zones 1/2/3 factor: These (integer) factors control by how much the wake is coarsenend in between the different wake zones. A factor of 4 means that when transitioning from one zone to the next 4 wake elements are replaced by a single wake element to coarsen the wake resolution (see :numref:fig-wakezones`.png`).
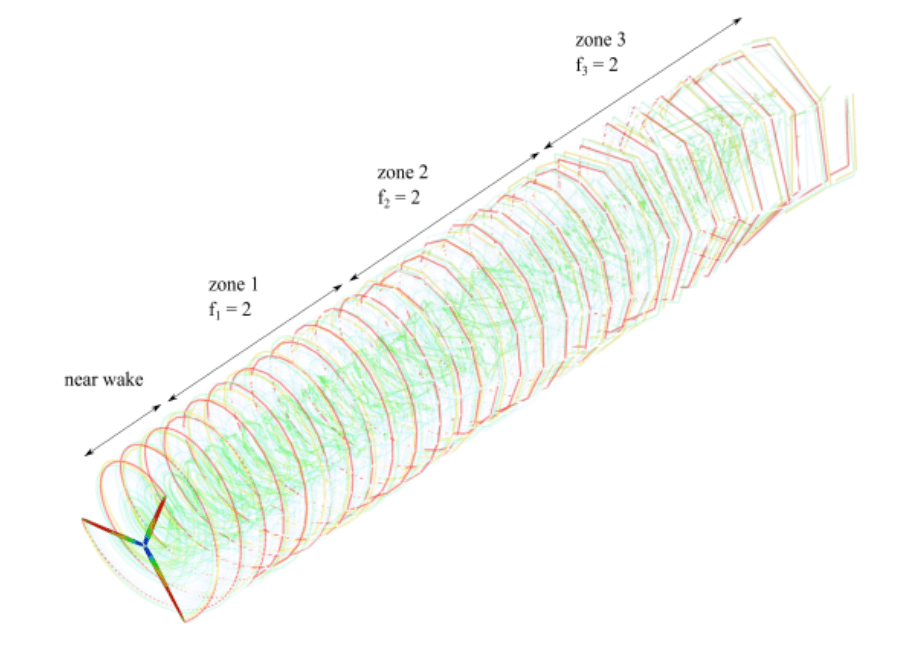
Fig. 71 Visualization of the wake zoning approach.
Vortex Modelling
Fixed Bound Core Radius (% Chord): This sets the fixed core radius of the bound blade vortices. Defined as a fraction of the local blade chord.
Initial Wake Core Radius (% Chord): This sets the intial core radius of the free vortices that are created at the blades trailing edge. Defined as a fraction of the local blade chord.
Turbulent Vortex Viscosity: This value is used in the vortex core growth model, see Vortex Core Desingularization.
Include Vortex Stretching: This option activates vortex stretching, see Vortex Core Desingularization.
Maximum Vortex Stretching Factor: After the cummulative vortex strain rate has reached a value larger than this factor it is automatically removed from the wake.
Turbine Gamma Iteration Parameters
Relaxation Factor: This relaxation factor is used when the blade circulation is updated during the circulation iteration.
Max. Epsilon for Convergence: The convergence criteria for the blade circulation.
Max. Number of Iterations: The maximum number of blade circulation iterations that will be carried out.
- 1
A. Li, M. Gaunaa, G. R. Pirrung, A. Meyer Forsting, and S. G. Horcas. How should the lift and drag forces be calculated from 2-d airfoil data for dihedral or coned wind turbine blades? Wind Energy Science Discussions, 2022:1–40, 2022. URL: https://wes.copernicus.org/preprints/wes-2021-163/, doi:10.5194/wes-2021-163.
- 2
H. Glauert. Airplane Propellers, chapter Aerodynamic Theory, pages 169–360. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1935. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-91487-4_3.